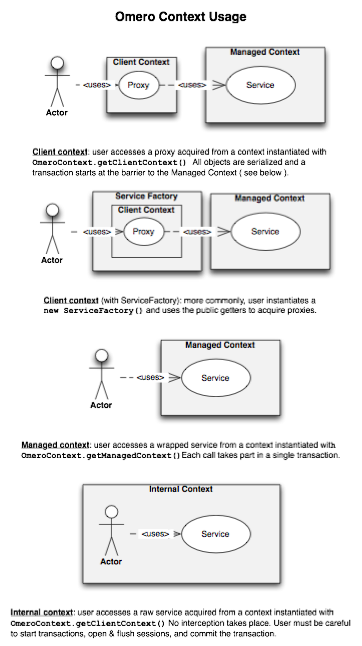
OmeroContext
The entire OMERO application (on a single JVM) resides in a single ome.system.OmeroContext. Each call belongs additionally to a single org.hibernate.Session (which can span over multiple calls) and to a single ome.model.meta.Event (which is restricted to a single task).
The container for all OMERO applications is the
OmeroContext
(https://github.com/ome/omero-common/blob/v5.7.0/src/main/java/ome/system/OmeroContext.java).
Based on the Spring configuration backing the context, it can be one of
client, internal, or managed. The use of a ServiceFactory
simplifies this usage for the client.
Hibernate sessions
A Hibernate Session comprises a
` Unit-of-Work <https://www.martinfowler.com/eaaCatalog/unitOfWork.html>`_
which translates for OMERO’s OME-Remote Objects model to a
relational database. It keeps references to all Database-backed objects so
that within a single session, object-identity stays constant and object
changes can be persisted.
A session can span multiple calls by being disconnected from the underlying database transaction, and then reconnected to a new transaction on the next call (see https://github.com/ome/omero-server/blob/v5.7.0/src/main/java/ome/tools/hibernate/SessionHandler.java for the implementation).
For information about Events see OMERO events and provenance.